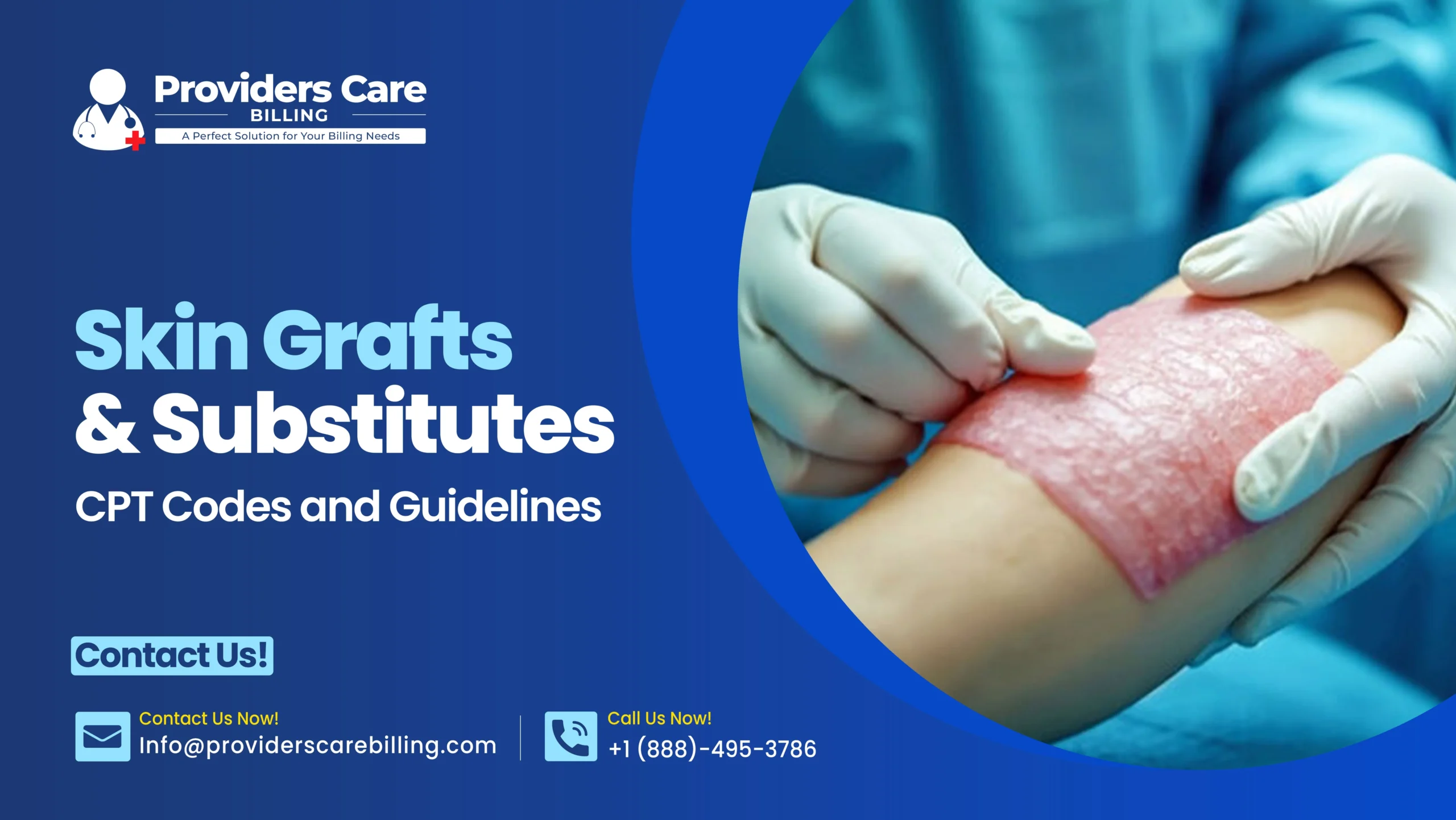
The data presented by the U.S. claims indicate that skin grafts and wound care operations are some of the 10 most commonly denied surgery claims. Such denials are not always caused by issues of medical necessity, but rather because of the wrong codes of CPT or the use of wrong modifiers. Among the surgeons, wound care experts, and billing team, understanding of the skin graft code is a crucial aspect to avoid losing revenue. Understanding correct CPT usage is only possible with expert medical billing services for wound care and surgical procedures.
Most of the practices that we work with at Providers Care Billing LLC experience an issue with billing split thickness skin graft CPT, full thickness skin graft CPT, and skin substitute CPT- particularly when add-on codes and calculations of surface area are required. This guide provides an understanding of the skin grafts and replaces the CPT codes and guidelines in a practical manner and clearly to help the healthcare provider to bill properly and receive a quicker payment.
Skin Grafts and Skin Substitutes in Medical Billing: What Are They?
Skin grafting is a surgical procedure that entails the transfer of skin from one part of the body to another to heal wounds, burns, ulcers, or surgical defects. Skin substitutes are natural or artificial substances that are used to facilitate the healing of wounds in cases where grafting cannot be done immediately. Medicare and commercial payers have unique CPT code families, documentation rules, and reimbursement guidelines for each service.
Skin Graft Coding Guidelines: What Every Provider Needs to Know
The following are the basic rules that should be followed before choosing a skin graft CPT code:
- Split or full graft thickness (code selection).
- Codes are to be reported according to the surface area of the recipient site.
- Preparation of the donor site is usually incorporated.
- Some of the CPT codes are add-on codes.
- Denials can be caused by the use of wrong modifiers.
The absence of such guidelines will lead to audits, downcoding, or nonpayment.

Split-thickness skin graft (STSG)
STSG consists of epidermis and a section of dermis, which are usually applied in burn management and treatment of chronic wounds.
Common STSG CPT Codes
- CPT 15100: Split -thickness skin graft.
- CPT 15101: For an extra 100 sq. cm.
Key Documentation Tips
- Wound size before grafting.
- Surgical technique.
- Medical necessity.
- Anatomical location.
CPT Codes of Full-Thickness Skin Grafts
Full-thickness grafts are full epidermis and dermis grafts, commonly applied in facial or hand reconstruction.
Normal Full-Thickness CPT Codes
- CPT 15260: Face, ears, eyelids, nose, lips, first 20 sq. cm full thickness of skin graft.
- CPT 15261: Code for extra 20 sq. cm.
Notes: In cases where the full-thickness code is used, the closing of the donor site is covered without any notes to the contrary.
Skin Substitute CPT Codes (15271–15278)
The skin substitutes are not reported in the same way as autografts are, and they are commonly put into the practice of advanced wound care.
- CPT 15271 -Application of skin substitute, first 25 sq. cm, trunk/arms/legs.
- Add-on per 25 sq. cm. extra.
- CPT 15275 and 15276 -Code for face, scalp, and extremities.
Poor reporting of 15275 is usual; records should specify the wound position.
CPT Code 4186 CPT CodeDescription (Skin Substitute Supply Code)
Q4186 is a specific product of skin substitutes, which is not considered an application code.
Billing requirement with Q4186:
- Product name.
- Size used.
- Waste documentation (where necessary).
A wrong combination of Q4186 and application codes often causes denials.
CPT 15004 is the code for Wound Bed Preparation
Wound bed preparation might be needed before grafting.
- CPT Code 15004 Surgical wound bed preparation.
- This code addresses the process of debridement and removal of necrotic tissue.
It should only be used independently when recorded as different and medically necessary.
CPT Code 15777 Implantation of Biologic Material
Indicators are used to apply biologic implants in soft-tissue reinforcement, not in typical skin grafts.
Care should be taken; harsh payer qualifications often need to be adhered to.
What Modifier Is Not Elaborated In Reporting Skin Grafts?
Shared Concern: Which modifier is not to be used?
- Modifier 50 ( Bilateral) – inappropriate.
- Modifier ‑51 (Multiple Procedures) – very many times redundant.
- Modifiers 59 ‑59 should be applied only in justifiable circumstances.
The abuse of modifiers is one of the major causes of claim audits.
Example
A case involved a clinic with CPT 15271 + 15272 skin substitute, which failed to record the wound size. Medicare denied the claim.
Upon rectification of documentation and reporting the surface area, the claim was re-filed, and 12000 dollars were reclaimed.
This shows how careful a choice of the CPT code should be. Providers should also follow CMS skin substitute billing guidelines to ensure compliance and avoid claim denials.
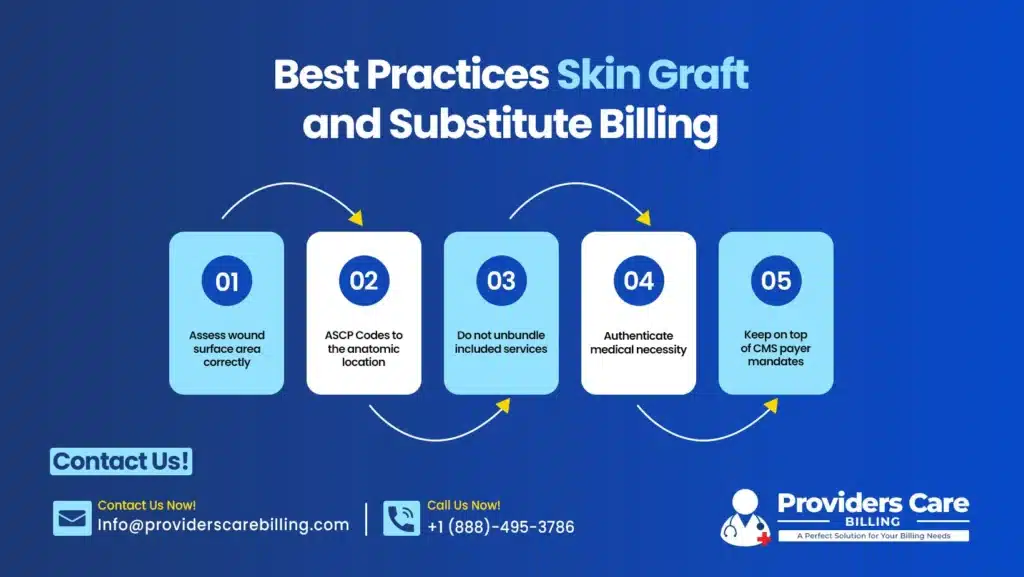
Best Practices Skin Graft and Substitute Billing
- Assess wound surface area correctly.
- ASCP Codes to the anatomic location.
- Do not unbundle included services.
- Authenticate medical necessity.
- Keep on top of CMS payer mandates.
Such practices minimize the number of audits and enhance the performance of revenue cycles.
Having skin-graft or wound-care billing issues?
Engage with reputable medical billing services in New York and across the USA firm so as to ensure that it optimizes reimbursements and remains audit-prepared. Book your free consultation.
Conclusion
Proper coding of skin grafts and substitutes will entail a profound understanding of the coding requirements, wound-care regulations, and payer specifications. CPT codes, such as split-thickness skin graft CPT codes to the skin substitute CPT 15271-1527,5 have a direct influence on reimbursement and compliance due to coding accuracy.
Cooperation with Providers Care Billing LLC will provide the providers with professional help in the sphere of medical bills, coding, credentialing, and revenue-cycle management, cleaner claims, reduced denials, and improved financial outcomes.
FAQs
How do you compare skin graft CPT and skin substitute CPT?
The use of skin grafts CPT codes is applicable to autografts; skin substitute CPT codes apply to biologic or synthetic products.
Is CPT 15004 billable with the codes for skin graft?
Yes, however, provided that the wound bed preparation is distinct and medically necessary.
Is CPT 15272 an add‑on code?
Yes, 15272 must be billed with 15271.
What is the modifier that is not used in reporting skin grafts?
The use of modifier -50 is not permitted in most cases.